Stop Mold : How Dew Point Control HVAC Solves Grow Room Humidity Issues
In cannabis grow room management, dew point control HVAC is now a common solution. Many growers depend on it, not just those using advanced technology. It gives better humidity control and helps fight a tough problem—mold.
Many cannabis growers share a common problem. Even with good dehumidifiers, crops can lose quality during flowering. This happens because of changes in humidity. Despite changing the watering schedules and adjusting the equipment, results are still unsatisfactory. In these cases, the issue might not be too little dehumidification. It could be a lack of “dew point control.”
We’re not trying to sell you anxiety. We want to help you see how important dew point control is for growing environments. We’ll cover what dew point is. We’ll also look at why traditional HVAC systems often don’t work well. Next, we’ll explain how dew point control HVAC systems function. We’ll look at how these systems help cannabis growers. They keep humidity steady, prevent mold, and save energy. You'll see how this technology is changing the game.
Are You Also Complaining About Mould in Your Grow Room?
Experienced cannabis growers know that mold problems are tough to get rid of. Mold doesn’t warn you before it strikes. It often shows up quietly on the undersides of leaves and deep inside buds, then spreads from there. Once it takes hold, it can result in reduced yields or even total crop loss.
You’re often doing everything right. You manage humidity levels, adjust airflow, and disinfect regularly. Yet mold still persists. Many cannabis growers often ask: Why do I see normal humidity readings, but mold still shows up?
This is not uncommon. Traditional humidity management methods often fail to show the true moisture level in the air. So, they can't help you know when the risk of mold increases. This is why we are discussing “dew point control” today.
Inaccurate Dehumidification Triggers Mold Growth
Traditional dehumidification methods primarily focus on adjusting humidity levels based on readings. What they lack is a mechanism that can truly sense the moisture state of the air. Humidity is merely a result, not the root cause. Without accurate dehumidification, you're essentially opening the door to microbial growth.
Mold thrives in damp conditions, especially in high-humidity, high-temperature environments. In cannabis grow rooms, the air gets cooler at night when the lights go off. But moisture in the air isn't quickly removed. Moisture gathers on cannabis plants, in corners, and near pipes. This creates a perfect spot for mold to grow.
Right now, your equipment might show the humidity is fine. But the real heat and humidity could be too high. The danger has arrived unnoticed.
RH ≠ Accurate Control: Traditional HVAC Lacks Dew Point Strategy
Many devices called "humidity control" just offer a basic adjustment of relative humidity. Relative humidity changes with temperature. For example, turning on lights during the day raises the temperature. This causes the relative humidity to drop. Turning off lights at night cools the air. This causes relative humidity to rise.
Now, you can't determine the real moisture content in the air using just relative humidity.
Dew point temperature is different. It is the only direct indicator that tells you “how much water vapor is in the air.” Only by controlling dew point can you truly control humidity.
Traditional HVAC dehumidification solutions can't stabilize the environment. Even those with dehumidification functions fall short. They lack dew point control logic.

Why Traditional HVAC System Fail in Humid Grow Room
Traditional HVAC systems were designed for human comfort, not plant growth. Their operational logic is simple temperature regulation and basic humidity control. In humid and heavy-load places like cannabis grow rooms, problems often arise. These include “slow response” “poor dehumidification” and “weak nighttime recovery”.
You can see this especially when humidity changes quickly. This happens during light cycle shifts, late flowering, and after heavy watering. Traditional HVAC systems can dehumidify too much, making the air too dry. They can also respond too slowly, which allows mold to thrive. Their control mechanisms are “sluggish” and often “superficial”.
Real Grower Feedback: Humidity Swings Ruined Flowering
We talked to a cannabis grower in California. He had three industrial dehumidifiers in his grow room. Still, he faced mold problems for weeks during the flowering stage. He said, “During the day, the humidity felt fine. But by night, it was like fog rolled in. Several cannabis plants then developed mold on their tops.”
Similar feedback is not uncommon. A Canadian customer shared, “This dew point control HVAC system works like an air manager. It doesn’t wait for humidity to rise. Instead, it predicts and adjusts based on dew point. Now, mold has nearly vanished.”
These cases show a common problem. Traditional systems find it hard to adapt quickly to changes in the environment. In contrast, dew point control HVAC systems can tackle the issue before it happens.
Grow Rooms Need Dew Point Control HVAC
Traditional equipment doesn’t meet the humidity needs of cannabis growers. So, what’s the solution? The answer is: implement a dew point control HVAC system.
This system monitors the dew point temperature in real time. It calculates the dew point for each rise in humidity. Based on the dew point difference, it decides how many systems to activate for dehumidification.
It coordinates the compressor, fan, and dehumidification unit to control humidity precisely. Instead of waiting to "see wet," it "anticipates wet" to take action quickly.
For growers seeking high quality, big yields, and fewer diseases, dew point control HVAC is more than better equipment. It’s a fresh way of thinking. You'll no longer be reacting to humidity changes; you'll be in control of the moisture in the air.

Understanding Dew Point Control
Many cannabis growers focus only on relative humidity (RH) for humidity management. But they often overlook another important factor: dew point. People who know how to control moisture in the air focus on dew point, not surface humidity. The dew point is key for humidity stability. It affects mold control and VPD balance.
So what is dew point? How does it differ from RH? And what factors influence dew point changes? Let's break it down step by step.
What is Dew Point?
Dew point is the temperature at which air begins to “condense.” When air cools down, moisture in it condenses. This means it changes from gas to liquid, creating water droplets. This temperature is the dew point.
We can think of dew point as the “saturation threshold” for air. When the temperature drops below this point, the air can't hold more water vapor. Then, it starts to condense. When the air temperature in a cannabis grow room nears the dew point, condensation may form. This can happen even if the relative humidity seems low. It may appear on leaves and walls. If left unchecked, mold will take advantage of the situation.
Dew point shows how humid the air is better than relative humidity. It helps us understand if it feels humid and if there might be any problems.
Dew Point vs Relative Humidity: Which One Matters More in HVAC?
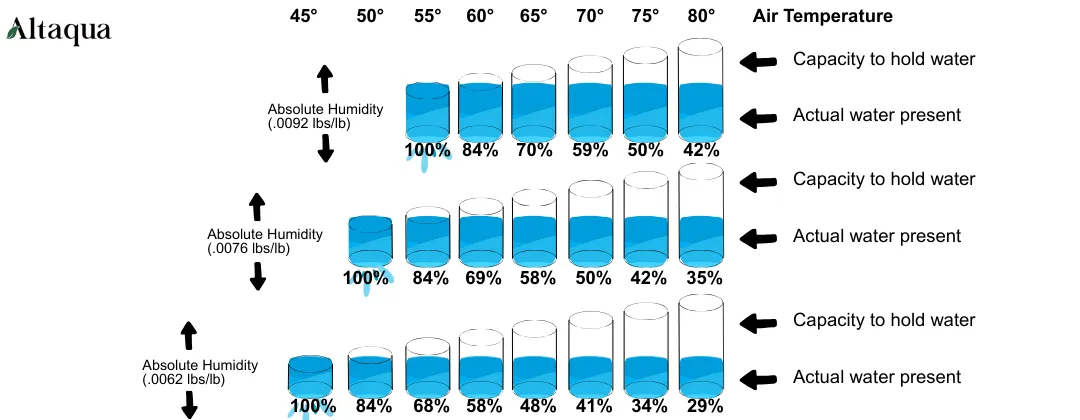
In HVAC control, only focusing on RH is like seeing a color-adjusted photo. It makes it tough to know what's real. But dew point is different; it's like a real ruler that quantifies the actual state of the air.
Relative humidity is a “relative value” that changes with temperature. For example, as the day warms up, humidity goes down. This makes it feel like the air is drier. However, the actual amount of water in the air hasn't decreased; it's just that the air has expanded.
Dew point, however, is an “absolute value.” It tells you exactly how much water vapor is present in the air. Regardless of temperature fluctuations, it reflects the air's “moisture-holding capacity.”
|
Sports event |
Relative Humidity (RH) |
Dew Point |
|---|---|---|
|
Define |
Ratio of water vapor content in the air to the maximum amount of water vapor that can be accommodated |
The temperature at which water vapor in the air cools to saturation and begins to condense |
|
Characteristic |
Relative values, temperature dependent |
Absolute value, independent of temperature, indicating actual moisture content |
|
Change with temperature |
Temperature rises → RH decreases (even if water vapor content remains unchanged) |
Temperature independent, reflecting actual moisture content |
|
Applied value |
Easily misjudged humidity conditions |
More accurate reflection of air humidity, suitable for precise control of humidity levels |
|
Role in HVAC control |
Aided judgment, needs to be understood in relation to temperature |
Core reference indicator for precise adjustment of system dehumidification or humidification requirements |
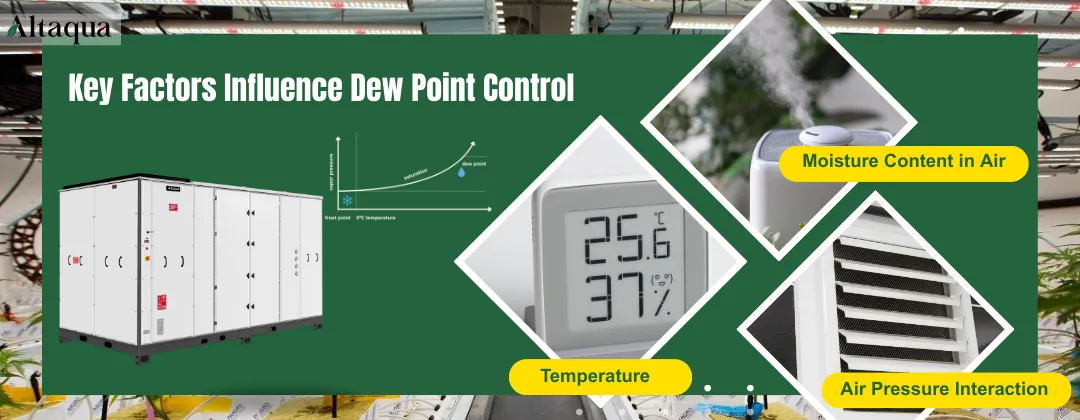
Key Factors Influence Dew Point Control HVAC
To control dew point, you must first understand the factors that influence it. There are three main factors: temperature, air humidity, and air pressure. These factors interact with each other.
Temperature
The higher the temperature, the more water vapor the air can hold, and the higher the dew point. Conversely, the lower the temperature, the less water vapor the air can hold, and the lower the dew point. An HVAC system that only controls temperature can face issues. When cooling, the temperature might drop below the dew point. This can lead to condensation.
Moisture Content in Air
This is the “basic ingredient” of dew point. The higher the moisture content in the air, the higher the dew point temperature. Even if the temperature stays the same, the dew point will rise. This happens as water enters the air from watering or evaporation.
Air Pressure Interaction
Airflow in a grow room can change local air pressure. This change affects the air's saturation point. If airflow is too slow, some corners may not get enough air. This can raise local pressure. As a result, the dew point gets closer to the actual temperature, leading to local condensation.
A scientific HVAC system must consider these three factors fully. It should not just react when RH is too high.
Why Dew Point Control HVAC Is Essential in Grow Room
Cannabis grow rooms have high humidity. They need careful control because even a small amount of water in the air can affect the flowers' health. Dew point control systems are designed specifically for such extreme environments.
For HVAC systems with dew point control, dehumidification aims to reduce moisture in the air. It's not just about lowering relative humidity.
It's not just about “removing moisture.” It’s crucial to know when to dehumidify, how much to take out, and how to manage airflow and temperature. This all depends on the dew point temperature. The goal is to keep the entire area in a “no condensation, no mold” safe zone.
Link Between Dew Point and VPD
VPD, or Vapor Pressure Deficit, is key for cannabis. It affects how the plant absorbs moisture and how intensely it breathes. VPD is found by subtracting the air dew point from the leaf temperature.
If the dew point is unstable, VPD fluctuates wildly. Cannabis struggles with changing conditions. This can lead to excessive moisture loss. It can also slow down transpiration and nutrient transport. As a result, growth and yield suffer.
Stabilizing dew point means stabilizing VPD. Cannabis needs VPD to stay in a good range to keep normal metabolic rhythms. This helps ensure full flowering and rich flavor.
Stable Dew Point = Stable RH Day & Night
Traditional HVAC systems can reduce humidity during the day. At night, they react passively to sudden spikes in humidity.
Traditional HVAC systems dehumidify during the day and respond slowly to humidity spikes at night. In contrast, HVAC with dew point control tracks the air's dew point in the grow room all the time.
When the dew point approaches saturation, it calculates the dew point value for each humidity rise. This helps determine how many systems to activate for dehumidification based on the dew point differences.
This continuous, proactive humidity control minimizes day-night humidity fluctuations in cannabis grow rooms. For cannabis, this is the most stable “climate assurance.”

How Dew Point Control HVAC Works in Cannabis Grow Room
Many cannabis growers believe "dew point control" is just about "dehumidification." But it's actually much more complicated.
Dew point control is a change in thinking. Instead of waiting for humidity to rise, we now anticipate risks. This lets us act wisely and step in before problems occur. This technology makes cannabis grow rooms better. It creates a stable, smart, and ideal environment for growing cannabis.
Dew Point Control ≠ Simple Dehumidification
Traditional dehumidifiers are straightforward. They turn on if the relative humidity (RH) is too high. Then, they shut off when RH drops below the set point.
This approach often falls short, especially during watering or when nighttime temperatures drop. This leads to big changes in relative humidity (RH). The system does not respond quickly. This causes problems such as localized condensation and mold growth.
Dew point control systems are like “checking the weather forecast” instead of “reading a thermometer.” They don’t get confused by relative humidity. They keep checking the air's moisture and temperature. This helps them know when they are close to the saturation point. When the dew point approaches, the system steps in to keep humidity safe.
Real-Time Dew Point Sensing for Precision Humidity Control
The “brain” of the entire HVAC system is the sensor. Our system uses precise temperature and humidity probes from E+E, based in Austria.
They operate in temperatures from -40°C to +60°C. Humidity accuracy is ±2.5%, while temperature accuracy is ±0.3°C. Our PLC system gathers this data and calculates the dew point. It then shows the results in real time on the touchscreen.
Our system can quickly spot humidity risks, even when conditions change fast. This includes heavy irrigation or sudden drops in nighttime temperatures. The PLC's internal logic control changes based on dew point values. This optimizes the dehumidification mode to keep humidity levels stable.
This process needs no human help. Growers don't have to keep watching RH values for possible exceedances. After setting the target range, the system automatically judges, executes, and adjusts. This keeps a stable growing environment for the plants.
Coordinated Dehumidification Based on Dew Point
Our humidity control is not by relative humidity, but by dew point temperature,the latter is more sientific. As the purpose of the dehumidification is to decrease the water contents in the air, not just lower the relative humidity level.
For the simple standalone dehumidifier, since there is no temperature control , the only way to control is by relative humidity, however, for your grow room ,not only you need to control the humidity level, you need to control the temperature.
For example, if your target is 70F/60%RH( dew point temp is 55F, water contents in the air is 9.3g/kg), your current condition is 82F/50%RH( dew point temp is 62F ,water contents in the air is 11.8g/kg) , As you could see, since the dew point and the water contents is higher on your current condition, so for our Grow Room HVAC System , the dehumidifier should work.
But for the standalone dehumidifier, since their control way is by relative humidity ,so it will not start as your current condition 50%RH which is lower than target 60%RH.
Integrated Compressor & Controller Work Together
The system’s efficiency lies in both judgment and execution. Our HVAC system uses a Siemens PLC as the "brain." It connects compressors, fans, and controllers in a closed-loop setup. This setup works under the PLC's unified command.
On the touch screen, users set the target temperature and humidity. The PLC then calculates the target dew point. It compares this with the real-time dew point from the system. If the actual dew point is higher than the target, the system starts one or more compressors for dehumidification.
This coordinated control focuses on dew point as the main indicator. It boosts dehumidification efficiency and accuracy. Also, it extends equipment life. This way, the planting environment achieves "smooth temperature and humidity, rapid response."
Why Dew Point Control HVAC Is a Game Changer
Traditional greenhouse environmental control systems typically regulate temperature and relative humidity. However, in the increasingly precision-demanding field of cultivation, this approach often falls short.
Dew point control in HVAC systems changes the game for precision. It goes beyond just humidity control. Instead, it offers true humidity stability and steady-state control.” It improves the growing environment for cannabis. It also lowers disease risk and energy costs. These changes greatly impact the cannabis cultivation industry.

Precise Humidity Stability for Healthy Plant Growth
The roots, stems, and leaves of plants have different sensitivities to humidity at different stages. Even slight fluctuations can affect transpiration, nutrient absorption, and even trigger stress responses.
Traditional humidity control systems can be easily impacted by daily temperature shifts and wind speed. This leads to fluctuations in RH. Dew point-controlled HVAC systems look at the moisture in the air. They protect against temperature changes and keep the environment stable and comfortable.
This stable humidity helps keep VPD (vapor pressure deficit) in the right range. It also ensures that plants stay in a comfortable “climate zone” during their whole life cycle.
Dew point control systems respond quickly to changes in humidity. They help manage vigorous transpiration in the vegetative growth stage. During flowering, they also handle high humidity sensitivity. This prevents “humidity shocks” that can disrupt crop rhythms.
Mold and Pathogen Prevention with Dew Point Control HVAC
Many diseases do not come from high heat or humidity. Instead, they often result from too much moisture in the air. This dampness creates a perfect home for mold, bacteria, spores, and other germs.
Dew point control HVAC uses “moisture content” as the basis for decision-making. It detects when the air is nearly saturated. Then, it steps in to reduce humidity. This keeps condensation and mold from forming.
At night, when temperatures drop and humidity rises, traditional systems respond slowly. Our system, however, quickly calculates the dew point for each humidity increase. It decides how many units to turn on for dehumidification. This is based on the difference between the target and current dew point values.
This early warning feature reduces "wet and cold" conditions in key spots like leaves, branches, and trunks. As a result, it significantly lowers the chances of diseases like powdery mildew, gray mold, mildew, and root rot.
Energy Efficiency & Lower Operational Costs
Precise control is key for optimal growing conditions. It is also necessary for energy efficiency. Traditional systems often focus on “safety” instead of “efficiency.” They frequently start and stop compressors, run fans at high power, and adjust for humidity changes. This all leads to much higher energy use.
The dew point control system checks and analyzes trends. It optimizes dehumidification cycles. This reduces waste and cuts down on unnecessary operation.
For example, if the PLC sees a high dew point but notes a slowing upward trend, it may just need to lower the fan speed. This can help with dehumidification without turning on multiple compressors. When the dew point rises rapidly, the system will flexibly increase dehumidification capacity.
This “demand-based allocation” system cuts power use. It also helps core parts, like compressors and fans, last longer and need less maintenance.
In medium to large cultivation rooms, saving on operational costs over time is significant.
Case Study: Dew Point Control HVAC in a Real-World Plantation
Dew point control systems sound advanced, but are they truly effective in actual cultivation? In this section, we share a real-world case study from a U.S. customer.
Project Background
The cultivation facility is in the northeastern United States. It has six cannabis flowering rooms. Each room measures 25 feet by 64 feet and stands about 10 feet tall. This totals 9,600 square feet for cultivation. Each flower room has about 740 plants. They release a lot of humidity while flowering.
At first, they had a standard system for controlling temperature and humidity. They also used several separate dehumidifiers. Growers noticed that when the relative humidity (RH) hit about 60%, it often “suddenly spikes.” This caused mold spots during flowering and resulted in unstable yields.
Solution: Dew Point Control HVAC
After a thorough evaluation, the customer decided to use the Altaqua Grow Room HVAC system for dew point control. Each system has E+E high-precision probes. These probes watch temperature and humidity all the time. They also calculate the dew point using internal PLC logic. Dew point is a key factor for decision-making.
Once the system is set up, users can quickly adjust the target temperature and humidity using the touchscreen. The PLC then takes over and manages automatic control.
- Whether to start the compressor
- How many compressors to start
- Adjusting airspeed and airflow
The entire operation process requires no manual intervention.
Performance:
After three months of system operation, the customer provided key data feedback:
Big boost in humidity stability: The dew point control system cut RH changes from ±8% to ±2%. It also quickly stabilized after peak flowering irrigation.
Big improvement in disease control: About 1 in 3 crops had gray mold before we started. Now, 6 batches have been deployed without any mold outbreaks.
Reduced energy use by 12-15%: The system stops ineffective dehumidification. It starts and stops as needed, cutting compressor runtime. This also lowers overall electricity costs.
The planting manager said, "This system works like autopilot for our environmental management.. We no longer worry about sudden humidity spikes at night. We can plant with peace of mind and harvest with confidence."

*Note: The data and results in this case study come from a real cultivation facility. They are typical, but they don’t promise the same results for every grower. Cannabis strains respond differently to their environment. The size and layout of grow rooms, along with local climate, can affect how well HVAC systems work. So, when choosing system setups or looking at expected results, it's best to do a full assessment that fits your specific growing environment. If needed, we can provide customized solution recommendations.
Conslusion
Today’s cannabis farming requires precise humidity control. It's not enough to be "close enough." A scientific, stable, and innovative approach is essential. Traditional HVAC systems focus on relative humidity control. However, they often struggle to adapt to quickly changing cultivation environments.
HVAC systems using dew point temperature as a control benchmark can better manage air moisture. They avoid drastic humidity changes, which helps reduce mold and diseases. This ensures healthy plant growth at all stages.
In this blog post, we covered dew point and how it differs from relative humidity. We also looked at the basics of dew point control systems used in farming. We showed how dew point control HVAC systems work in real cultivation chambers. They helped growers get steadier yields and better quality. Plus, they cut down on energy use and operational costs.
If you want to manage your crops better and get top-quality results, a dew point control HVAC system is a great upgrade to think about.
FAQ
1. My growing room is already equipped with a traditional HVAC system. Is it necessary to replace it with a dew point control system?
If your system struggles to maintain stable humidity during big changes, like after watering or temperature shifts, you may want to upgrade. Also, if you often deal with mold and VPD issues, it's a good idea to consider this upgrade. A system with dew point control can greatly improve your situation.
2. Will a dew point control system increase my energy consumption?
Dew point control systems use smart interlocking controls. They operate equipment based on real needs. This avoids unnecessary dehumidification and overuse. As a result, they help save energy and lower costs over time.
3. Why can't we just rely on RH for control?
Relative humidity can change with temperature. It might seem normal, but the air could already have too much moisture. Dew point is a clear and steady measure of humidity. It helps the system know when to dehumidify and by how much. This way, it avoids both over- and under-dehumidification.
4. How do I know if my growing room is suitable for a dew point control system?
Check these factors: Do you notice sudden humidity spikes in your growing room at night or after you ventilate? Are there persistent mold issues? Is there over-control of humidity, resulting in plants being “dried out”? If you face similar issues, it's best to reach out to a professional team. They can assess the environment and decide if a dew point control system will work for you.
Share with your friends:
Popular Blogs on Altaqua:
Download Catalogue





